File:SG RLS LMS chan var.png
From Vigyanwiki
SG RLS LMS chan var.png
SG_RLS_LMS_chan_var.png (561 × 420 pixels, file size: 12 KB, MIME type: image/png)
This file is from Wikimedia Commons and may be used by other projects. The description on its file description page there is shown below.
Summary
| DescriptionSG RLS LMS chan var.png |
English: Developed according to TU Ilmenau teaching materials.
clear all; close all; clc
%% Initialization
% channel parameters
sigmaS = 1; %signal power
sigmaN = 0.01; %noise power
% CSI (channel state information):
% the channel for the transmission of the first NS1 training symbols
channel1 = [0.722 - 0.779i; -0.257 - 0.722i; -0.789 - 1.862i];
% the channel for the transmission of the next NS2 training symbols
channel2 = [-0.831 - 0.661i;-1.071 - 0.961i; -0.551 - 0.311i];
M = 5; % filter order
% step sizes
mu_LMS = [0.01,0.07];
mu_SG = [0.01,0.07];
% symbols / ensembles
NS1 = 500;
NS2 = 500;
NS = NS1+NS2;
NEnsembles = 1000; %number of ensembles
%% Compute Rxx and p
%the maximum index of channel taps (l=0,1...L):
L = length(channel1) - 1;
H = convmtx(channel1, M-L); %channel matrix (Toeplitz structure)
Rnn = sigmaN*eye(M); %the noise covariance matrix
% Inline functions:
calc_Rxx = @(channel) ...
sigmaS*(convmtx(channel, M-L)*convmtx(channel, M-L)')+sigmaN*eye(M);
calc_p = @(channel) sigmaS*(convmtx(channel,M-L))*[1; zeros(M-L-1, 1)];
Rxx = zeros(M,M,2);
p = zeros(M,2);
A = calc_Rxx(channel1);
Rxx(:,:,1) = calc_Rxx(channel1);
Rxx(:,:,2) = calc_Rxx(channel2);
p(:,1) = calc_p(channel1);
p(:,2) = calc_p(channel2);
% An inline function to calculate MSE(w) for a weight vector w
calc_MSE = @(w, ch) real(w'*Rxx(:,:,ch)*w - w'*p(:, ch) - p(:, ch)'*w + sigmaS);
%% Adaptive Equalization
N_test = 2;
MSE_LMS = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
MSE_SG = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
MSE_RLS = zeros(NEnsembles, NS, N_test);
for nEnsemble = 1:NEnsembles
%initial symbols:
symbols1 = sigmaS*sign(randn(1,NS1));
symbols2 = sigmaS*sign(randn(1,NS2));
%received noisy symbols:
X1 = convmtx(channel1, M-L)*hankel(symbols1(1:M-L),[symbols1(M-L:end),zeros(1,M-L-1)]) + ...
sqrt(sigmaN)*(randn(M,NS1)+1j*randn(M,NS1))/sqrt(2);
X2 = convmtx(channel2, M-L)*hankel(symbols2(1:M-L),[symbols2(M-L:end),zeros(1,M-L-1)]) + ...
sqrt(sigmaN)*(randn(M,NS2)+1j*randn(M,NS2))/sqrt(2);
X = [X1, X2];
symbols = [symbols1, symbols2];
for n_mu = 1:N_test
w_LMS = zeros(M,1);
w_SG = zeros(M,1);
p_SG = zeros(M,1);
R_SG = zeros(M);
for n = 1:NS
if n <= NS1, curh = 1; else curh = 2; end
%% LMS - Least Mean Square
e = symbols(n) - w_LMS'*X(:,n);
w_LMS = w_LMS + mu_LMS(n_mu)*X(:,n)*conj(e);
MSE_LMS(nEnsemble,n,n_mu)= calc_MSE(w_LMS, curh);
%% SG - Stochastic gradient
R_SG = 1/n*((n-1)*R_SG + X(:,n)*X(:,n)');
p_SG = 1/n*((n-1)*p_SG + X(:,n)*conj(symbols(n)));
w_SG = w_SG + mu_SG(n_mu)*(p_SG - R_SG*w_SG);
MSE_SG(nEnsemble,n,n_mu)= calc_MSE(w_SG, curh);
end
end
%RLS - Recursive Least Squares
lambda_RLS = [0.8; 1]; %forgetting factors
for n_lambda=1:length(lambda_RLS)
%Initialize the weight vectors for RLS
delta = 1;
w_RLS = zeros(M,1);
P = eye(M)/delta; % (n-1)-th iteration, where n = 1,2...
PI = zeros(M,1); % n-th iteration
K = zeros(M,1);
for n=1:NS
if n <= NS1, curh = 1; else curh = 2; end
% the recursive process of RLS
PI = P*X(:,n);
K = PI/(lambda_RLS(n_lambda)+X(:,n)'*PI);
ee = symbols(n) - w_RLS'*X(:,n);
w_RLS = w_RLS + K*conj(ee);
MSE_RLS(nEnsemble,n,n_lambda)= calc_MSE(w_RLS, curh);
P = P/lambda_RLS(n_lambda) - K/lambda_RLS(n_lambda)*X(:,n)'*P;
end
end
end
%% Wiener Solution
MSE_Wiener(1:NS1) = calc_MSE(Rxx(:,:,1)\p(:,1),1);
MSE_Wiener(NS1+1:NS) = calc_MSE(Rxx(:,:,2)\p(:,2),2);
MSE_LMS_1 = mean(MSE_LMS(:,:,1));
MSE_LMS_2 = mean(MSE_LMS(:,:,2));
MSE_SG_1 = mean(MSE_SG(:,:,1));
MSE_SG_2 = mean(MSE_SG(:,:,2));
MSE_RLS_1 = mean(MSE_RLS(:,:,1));
MSE_RLS_2 = mean(MSE_RLS(:,:,2));
figure(1)
n = 1:NS;
m= [2 4 6 10 30 60 100 300 600 1000];
semilogy(m, MSE_LMS_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
hold all;
semilogy(m, MSE_LMS_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(m, MSE_SG_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(m, MSE_SG_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(m, MSE_RLS_1(m),'+','linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(m, MSE_RLS_2(m),'o','linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(n, MSE_Wiener(n), 'color','black','linewidth',2);
semilogy(n, MSE_LMS_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(n, MSE_LMS_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','blue');
semilogy(n, MSE_SG_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(n, MSE_SG_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','red');
semilogy(n, MSE_RLS_1(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','green');
semilogy(n, MSE_RLS_2(n),'linewidth',2, 'color','green');
grid on
xlabel('Ns');
ylabel('MSE');
title(['LMS, SG, RLS, \sigma_N= ' num2str(sigmaN) ', \sigma_S= '...
num2str(sigmaS) ', M= ' num2str(M) ', L= ' num2str(L) ]);
legend(['LMS, \mu=' num2str(mu_LMS(1))],['LMS, \mu=' num2str(mu_LMS(2))],...
['SG, \mu=' num2str(mu_SG(1))],['SG, \mu=' num2str(mu_SG(2))],...
['RLS, \lambda=' num2str(lambda_RLS(1))],['RLS, \lambda=' ...
num2str(lambda_RLS(2))],'Weiner solution',2);
axis([0 NS 0.002 1])
|
| Date | |
| Source | Own work |
| Author | Kirlf |
Licensing
I, the copyright holder of this work, hereby publish it under the following licence:
This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International licence.
- You are free:
- to share – to copy, distribute and transmit the work
- to remix – to adapt the work
- Under the following conditions:
- attribution – You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the licence, and indicate if changes were made. You may do so in any reasonable manner, but not in any way that suggests the licensor endorses you or your use.
- share alike – If you remix, transform, or build upon the material, you must distribute your contributions under the same or compatible licence as the original.
Captions
Add a one-line explanation of what this file represents
The mean square error perofrmance of Least mean squares filter, Stochastic gradient descent and Recursive least squares filter in dependance of training symbols in case of changed during the training procedure channel.
Items portrayed in this file
depicts
2 March 2019
image/png
File history
Click on a date/time to view the file as it appeared at that time.
| Date/Time | Thumbnail | Dimensions | User | Comment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| current | 00:35, 16 July 2019 | 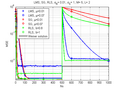 | 561 × 420 (12 KB) | wikimediacommons>Kirlf | Noise power are fixed in the signal model. |
File usage
The following page uses this file:
Metadata
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitise it.
If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.
| Horizontal resolution | 37.8 dpc |
|---|---|
| Vertical resolution | 37.8 dpc |
| File change date and time | 19:02, 15 July 2019 |
| Software used |
|
| Date and time of digitising |
|
Retrieved from ‘https://www.vigyanwiki.in/wiki/File:SG_RLS_LMS_chan_var.png’
